In our part of the world it is quite possible to join a Fish tapeworm to infect. The danger is particularly great with uncooked, raw fish that you have caught yourself.
What is fish tapeworm infection?
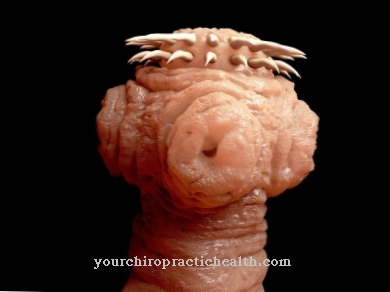
The fish tapeworm lives mainly in fresh water. Its intermediate hosts are small freshwater fish and crustaceans that are consumed by the final hosts of the fish tapeworm (larger predators, humans, dogs, cats and other fish-eating mammals).
The fish tapeworm Diphyllobotrium latum is mainly found in the inland lakes of the northern hemisphere. Brackish and freshwater fish such as trout, perch and pike are mostly infected with the fish tapeworm. The parasite nests in the internal organs, especially the liver, but also in the muscles and intestinal tract of the intermediate hosts.
Another subspecies - Diphyllobotrium pacificum - attacks humans, seals and sea lions as a definitive host and is particularly widespread in the Pacific region.
causes
The infection with the fish tapeworm occurs in humans, dogs and cats through the consumption of raw or insufficiently fried or heated fish. The most common type of fish tapeworm is Diphyllobothrium latum, which occurs mainly in the Baltic States, Russia, Scandinavia, Alaska and North America.
The parasite living in the intestines of the ultimate host can grow up to 15 meters long and have a lifespan of 10 years. The head of the fish tapeworm is provided with suction cups and a ring of hooks with which it attaches itself to the wall of its host's small intestine. The parasite is a hermaphrodite that sheds individual tapeworm limbs as soon as the fertilized eggs in these limbs have matured.
The fertilized eggs of the fish tapeworm get into the sewage with the feces, where they are ingested by intermediate hosts and the development cycle begins again from the fertilized eggs to larvae to fins and the sexually mature tapeworm in the intermediate and final hosts.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
An infection with the fish tapewum is usually symptom-free. In the first three to six weeks after infection, the larva develops into a fish tapeworm, which means that there are no symptoms. Only then does a fish tapeworm cause gastrointestinal complaints such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea in individual cases.
Occasionally, there is a loss of appetite, which is relatively quickly noticeable through weight loss. Although there are no other symptoms at first, a fish tapeworm requires medical treatment. Otherwise, the parasite can remain in the body for weeks, months or even years and cause chronic complaints. A vitamin deficiency often occurs, which manifests itself in the signs of anemia - paleness, rapid heartbeat, difficulty breathing and sudden sweats.
In the further course it can also lead to chronic gastrointestinal complaints. A fish tapeworm cannot be seen externally. However, the weight loss combined with the increasing feeling of illness indicates a condition that requires medical examination and treatment. In addition, an infection can often be traced back to the consumption of a certain food or contact with a possibly infected person or animal. This means that an infection can usually be diagnosed quickly and in a targeted manner.
Diagnosis & course
Freshwater fish infected with the fish tapeworm can contain viable larvae that pass to the ultimate host through consumption. The larvae of the fish tapeworm can survive even in fish that are frozen inadequately or only briefly. After the larva has been ingested, it takes about three to six weeks, depending on the stage of development of the larva, for the adult, sexually mature fish tapeworm to develop in the intestine of the final host.
The first symptoms such as gastrointestinal complaints, loss of appetite, bloating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and sudden weight loss only appear after the development of fish tapeworm has been completed. In many cases the infection with the parasite is symptom-free for many years and in some cases the fish tapeworm is the cause of a deficiency in vitamin B12, which can lead to anemia, heart problems and breathing problems.
Diagnosing fish tapeworm infestation is relatively easy. Since the tapeworm rejects individual limbs with sexually mature eggs in the intestine, these are easily detectable when examining the stool.
Complications
Fish tapeworm infection can lead to some complications if left untreated. The parasite can initially cause mild gastrointestinal complaints such as nausea and diarrhea. The associated loss of appetite can lead to significant weight loss. If left untreated, the tapeworm can enlarge and spread to the internal organs.
Possible late effects are inflammation of the gallbladder and pancreas, rarely also appendicitis and intestinal obstruction. If larvae form, severe skin diseases, epilepsy and damage to the skeletal muscles can occur. However, an infection with the fish tapeworm does not usually lead to the formation of larvae, unless there is a serious pre-existing disease.
However, the fish tapeworm's high vitamin B12 consumption can lead to deficiency symptoms. The result is rarely a slight anemia, which in turn is associated with complications. Typical symptoms of anemia are paleness, difficulty breathing and a high pulse. In general, serious complications rarely occur with a fish tapeworm infection.
Once diagnosed, a fish tapeworm can be removed 90 to 100 percent of the time without further discomfort. However, the prescribed drugs (praziquantel, niclosamide) can cause side effects such as muscle pain, loss of appetite and fatigue. Further complications can occur in patients with cardiac arrhythmias or impaired kidney or liver function.
When should you go to the doctor?
With a fish tapeworm, a visit to the doctor is always necessary. The disease does not heal by itself and can lead to various complications and complaints if left untreated. As a rule, the doctor should always be consulted if there are discomforts in the stomach or intestines after eating fish. A doctor should be consulted immediately, especially with raw and undercooked fish. Severe weight loss or loss of appetite can indicate the fish tapeworm. Nausea, diarrhea or severe stomach cramps are typical symptoms of this disease.
If these symptoms occur after eating or if they continue to occur without a particular reason, a doctor must be consulted. In acute emergencies or in very severe pain, an emergency doctor can be called or the hospital can be visited. As a rule, a visit to a general practitioner or a pediatrician is sufficient for fish tapeworms. The disease is treated with the help of medication and in most cases it leads to quick success. Since the affected person can contract a fish tapeworm again, a doctor must always be consulted if the symptoms of the disease occur.
Doctors & therapists in your area
Treatment & Therapy
Therapy against fish tapeworm is also relatively simple. The fish tapeworm can be easily killed with drugs such as praziquantel or niclosamide and is completely excreted in the stool. The prognosis for healing is good, because the tapeworm has usually completely disappeared after treatment with the worm-killing agent.
In very rare cases, fins can form in the body of the definitive host, making the treatment more protracted. An infection from person to person is not possible because the fish tapeworm needs the intermediate hosts for its development cycle.
The worming drugs require a prescription and, in a few cases, can lead to side effects such as stomach pain and nausea. The worming treatment must be carried out consistently so that all larvae are killed. In pregnant and breastfeeding women, the doctor must weigh up whether these drugs can be used.
Outlook & forecast
The prognosis for a fish tapeworm infestation is judged to be favorable. Almost 100% of the sick make a full recovery. If medical treatment is used, there is a significant improvement in health within a few days. The prescription drugs kill the worm.
Then it is independently transported away from the organism. The administration of medication can lead to side effects, which normally regress completely after discontinuing the medication. Consequential damage is only to be expected in the event of a worm infestation by the fish tapeworm if there were already severe health impairments before the start of therapy.
Without medical treatment, the patient's state of health can be impaired for a long time. The fish tapeworm has a lifespan of around 10 years and can reach a length of up to 15 meters in the human intestine. There is a decrease in wellbeing, weight loss and a reduction in performance. An alternative to drug treatment in the case of worm infestation has not yet been available to the extent required.
In spite of the good prospect of recovery, the consumption of raw fish can lead to renewed worm infestation in the course of life. The prognosis and the prospect of recovery are also favorable for a new disease.
prevention
As a preventive measure, it is recommended that freshwater fish always fry, cook or boil sufficiently. If the fish is heated for five minutes at approx. 60 ° C, all larvae are killed. Pregnant women in particular are often advised to avoid raw fish, which is mostly found in sushi. Cold also kills the larvae of the fish tapeworm. If the fish has been frozen for at least 24 hours at -18 ° C or 72 hours at -10 ° C, the tapeworm larvae cannot survive.
Aftercare
With a fish tapeworm, the options for follow-up care are relatively limited. The disease must first be treated completely, whereby of course the source of the fish tapeworm must be removed and should no longer be consumed. It is a relatively simple condition that can be treated by simple means.
There are usually no particular complications. Since the fish tapeworm can lead to nausea or diarrhea and vomiting, the stomach should be spared.The affected person is dependent on a gentle diet, whereby fatty or salty dishes are to be avoided. Since the fish tapeworm also leads to a high loss of water, the person affected should drink a lot, water or juices in particular being very suitable.
Even after the symptoms have subsided, the stomach should still be spared, so that the usual meals can only be taken a few days after the healing process. If the fish tapeworm is being treated with medication, it should be taken regularly. Possible side effects or interactions should also be discussed with a doctor. As a rule, the life expectancy of the person affected is not reduced by this disease.
You can do that yourself
A fish tapeworm always requires medical treatment. If you suspect an infestation, you should see a doctor directly - preferably with a stool sample. The doctor should be informed about possible causes, such as the consumption of fresh or brackish water fish, in order to facilitate the subsequent diagnosis of the fish tapeworm. Medical treatment can be supported by some home remedies and measures.
First of all, a balanced and slightly laxative diet is recommended. Fermented foods such as sauerkraut, cabbage and the like help ensure that the fish tapeworm is excreted quickly. In principle, foods with a high sugar content should be avoided in the event of a worm infestation.
By avoiding sweets, the fish tapeworm is deprived of its vital fungal environment and it quickly dies. This measure can be supported by homeopathic remedies. These include preparations such as Spigelia, Abrotanum and China, which are best taken in consultation with a doctor or an alternative practitioner.
Finally, sufficient intimate hygiene should be ensured. In addition, the exact cause of the fish tapeworm has to be determined in order to avoid re-infestation. A comprehensive anamnesis may be necessary for this.



.jpg)










.jpg)













