Of the Flat foot or Arched feet is, besides splayfoot, one of the most common foot malpositions. Above all, the longitudinal arch of the foot is strongly flattened, so that the foot as a whole rests almost completely on the floor when walking. Flatfoot is usually congenital, but it can also occur in the course of life as a result of orthopedic errors.
What is a flat foot?
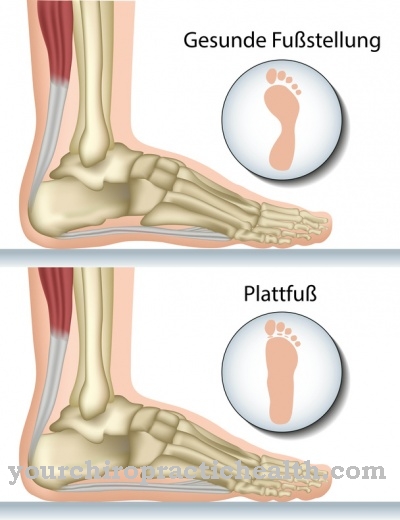
Many children already come with one Flat foot to the world. Because the flat tire, or technically exact Arched feet, predominantly occurs in childhood, a pediatrician or an orthopedic specialist can identify the predisposition to this at an early stage. Other people who suffer from this misalignment of individual foot bones have contracted this abnormality during their lifetime.
The foot lies flat on the sub-floor when the affected person is standing. The arch of the foot, which normally has a hollow shape, is not or hardly present in a flat foot, so that the foot can be pushed through and the normal static bulge from the ball of the forefoot towards the heel is missing. The symptoms that appear in flatfoot are an accompanying flat foot, a change in the edge of the foot in the form of a misalignment and painful symptoms that appear on the feet themselves, in the calves and other movement elements up to the back.
causes
A so-called innate Flat foot usually occurs in connection with other malformations of the bony areas and can have genetic causes. The acquired flat foot has many causes, including excessive body weight and poor footwear. In addition, abnormalities in flatfoot do not only consist in the bone changes themselves, but also in insufficient stability and performance of the so-called holding apparatus.
This applies in particular to insufficiently strong and impaired tendons, muscles and baths which cannot maintain a normal arch of the foot. In addition, a predominantly sitting posture, long standing, little movement and extremely reduced walking of children without shoes, for example in sand, contribute to the fact that a flat foot can occur due to insufficient stress on the holding units.
In addition, diseases such as rickets, poliomyelitis and diseases from the neurological and rheumatic areas can be considered as causes of flat foot.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
The symptoms of a congenital flat foot can be recognized shortly after birth. The foot shows a malposition in which the outwardly curved sole of the foot and the bent, upright heel are already clearly pronounced. In addition, the forefoot is splayed outwards. As a result, the children learn to walk relatively late.
Movement is restricted. Pain is common with age. Further complaints, especially pain, do not occur. The symptoms are different in the case of flat feet in adolescence. As a rule, severe stress pain occurs here. As a result, the young people affected develop a relieving posture and limp as a result.
Without therapeutic measures, a considerable restriction of movement can develop with increasing pain. In adults who develop flat feet, symptoms occur after a higher level of stress. These are primarily felt when the arch of the foot is lowered. When the sole of the foot is completely in contact, the pain goes away again.
The pain usually occurs on the sole of the foot and on the inner edge of the foot. However, due to the misalignment, pain in the knee and hip area can also occur. The intense stress on certain areas of the foot can cause pressure points and pressure sores, especially in overweight people. These also impair the ability to move and increase the sensation of pain.
Course of disease
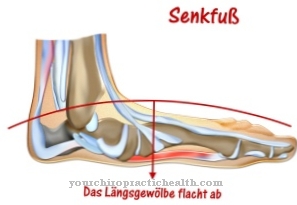
A Flat foot develops in the case of an acquired flatfoot from individual holding elements, which are actually responsible for the support, stabilization and maintenance of the anatomically normal arch of the foot and are only insufficiently developed.
As a result, the tension in these segments decreases and the arch of the foot sags over time if these areas are not strengthened and stressed.
As a result, there is an inadequate cushioning effect, so that all subsequent and surrounding bones and joints are subject to constant compression and this results in pain or changes in the foot. This appearance is known as arch arches and can be treated.
Complications
Flatfoot can cause a variety of complications. First of all, the misalignment of the feet is accompanied by rapid fatigue of the feet. Often there is pain and signs of wear and tear on the bones and joints. If the valgus deformation remains untreated, permanent joint damage and deformation can occur.
This is accompanied by pain and malpositions, which in turn are associated with complications. The knees, hips and spine, which are increasingly overstressed due to the misalignment of the feet, are also affected. This can lead to poor posture, overstretching of the ligaments and tendons and arthritic changes in the tarsal bones.
In general, the risk of osteoarthritis increases with flat feet. Possible consequences are headaches and chronic complaints. In the long term, a so-called walking foot can develop or further deformations such as a flat arched foot or splayfoot develop. Complications can also arise when treating flat feet.
A surgical procedure carries the typical risks and can cause bleeding and scarring. In rare cases, further misalignments can occur. The prescribed pain medication can cause side effects and interactions. Therapeutic measures such as insoles can encourage perspiration and, if used improperly, trigger further complaints.
When should you go to the doctor?
Flat feet can already exist at birth or develop in the course of life. However, in both cases it is advisable to see a doctor. An existing flat foot can be completely eliminated with a surgical procedure and subsequent follow-up care. If the affected person decides against such treatment, considerable complications can be expected. A flat foot can disrupt the entire movement, so that the affected person can complain of severe pain.
If medical treatment is consistently avoided, permanent consequential damage can also occur. Going to the doctor can no longer be avoided, because this is the only way to heal or recover without complications. If not treated, there is also the risk that the foot will be misaligned. The result: Sharp pain with even the smallest of movements, so that normal movement is not possible. These symptoms can only be alleviated and permanently eliminated with appropriate treatment.
Treatment & Therapy
Treating a Flat foot or Arch arches is always possible and ideally consists of both passive and active treatment. Active therapy is based on regular, healthy use of the foot muscles and targeted physiotherapy exercises. These contribute to strengthening the holding apparatus and can both support freedom from pain and ensure partial regression of the flat foot and the associated deformities.
In the passive treatment of a flat foot, the orthopedic surgeon uses the possibilities that can be implemented with suitable footwear to achieve an artificial stabilization of the arch of the foot. This therapy usually involves wearing orthopedic insoles. Some sufferers who complain of massive flat feet with pain in the back as a result of surviving illnesses are treated using an operative method. This is usually only considered from the age of eight and shows good results.
Aftercare
As a rule, there is no follow-up care for a flat foot. This is either because the flatfoot exists, but is not a restriction or could be surgically corrected. Since there are no signs of complaints, there is no need for scheduled examinations. Instead, the patient presents if there are acute signs.
Sick people can actively contribute to preventing a new flat foot or to counter the further development of a diagnosed malalignment. You will be informed about suitable measures in an interview. Patients usually have to wear insoles to avoid complications.
In severe cases, doctors also prescribe orthopedic shoes and physiotherapy to strengthen the muscles. In everyday life, those affected should avoid putting too much strain on their feet and prefer varied movement sequences. If people with flat feet have to use orthopedic aids on a permanent basis, they will need new prescriptions on a regular basis.
The doctor then uses the opportunity to ascertain the status of the deformity. An assessment is usually sufficient for this. In certain cases, the situation can also be analyzed with a modeling clay, an electronic measuring plate or an X-ray image. Depending on the severity of the disease, doctor and patient can agree on an individual rhythm for further presentations.
You can do that yourself
In order to live better with flat feet in everyday life, there are shoe insoles that are specially adapted to the shape of the foot. They support the arch of the foot and distribute the load. Depending on the extent of the discomfort, custom-made orthopedic shoes are even more helpful in coping with everyday life despite flat feet.
In addition to these commercially available means, simple exercises that can easily be incorporated into everyday life also help. A few minutes of regular exercise are enough to alleviate the symptoms. In general, all physiotherapy exercises that strengthen the lower leg and foot muscles and the structure of the arch of the foot are helpful. In order to achieve the best effect with the training, the exercises are performed barefoot. As soon as the execution becomes painful, it must be stopped. Below are two sample exercises.
Tip toe: During this exercise, the person concerned stands up hip-width apart if the knees are not fully depressed. Then both heels are pressed off the floor, held in this position for ten seconds and then slowly rolled back onto the floor. The process is repeated three to five times. Different solid surfaces increase the training effect.
Cloth gripper: A cloth, for example a tea towel, is spread out on the floor. While sitting or standing, the patient clamps the cloth between toes and balls of the feet. Then it is held in the air for five seconds. This exercise is performed up to ten times with each foot. With consistent training, the weight of the towel increases.



.jpg)










.jpg)













