Corticosteroids, or also Corticoids or Steroid hormones are endogenous hormones. An imbalance in the form of a shortage or overproduction can have serious consequences for the human organism.
What are Corticosteroids?
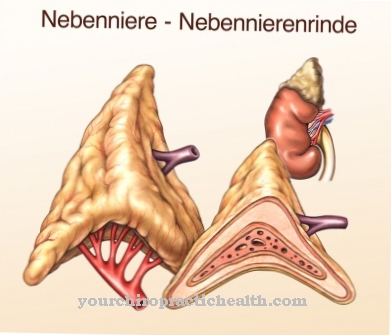
Corticosteroids are produced in the adrenal cortex and are the body's own hormones. They are one of about 50 groups of steroid hormones formed in the adrenal cortex.
Constant production is essential for the body. For example, the important cortisone and cortisone-like substances have been produced artificially for around 40 years. They are hormone-like and have a much stronger effect than the corticosteroids produced by the body.
The most well-known corticosteroid is cortisone. It regulates numerous metabolic processes in the body. Artificially produced, it has long been considered a “miracle drug” against all diseases. Today we know about its effects, but also side effects and use cortisone much more carefully.
Medical application, effect & use
Corticosteroids are used, among other things, for the treatment of asthma, eczema, epilepsy, neurodermatitis, rheumatic diseases, inflammatory bowel diseases, certain chemotherapies as well as various skin diseases (e.g. psoriasis).
The glucocorticoids in particular have a significant effect on immune diseases and emergency situations. They play a particularly important role in therapeutic applications. In this way, a blockage against inflammatory processes can be built up when ingested. In addition, they suppress the formation of connective tissue and stabilize the circulation in the event of a shock. In the body, they stimulate the production of stomach acid and have an effect on the immune system.
Natural corticosteroids are much weaker than the artificially produced corticosteroids. With the same drug concentration, they also bind more easily to receptors. Corticosteroids also have anti-inflammatory, antiallergic and immunosuppressive effects. Great care must be taken when administering corticosteroids, especially glucocorticoids. Due to its high effectiveness, it should only be taken after careful examination, at the lowest possible dose and for a short time.
If long-term treatment with corticosteroids is necessary, the dose and the exact intake must be strictly adhered to. Patients should neither change the dose nor discontinue therapy on their own initiative. This can lead to an acute relapse. Corticosteroids can be used in the form of tablets, infusions and syringes, as well as ointments, creams and sprays.
Skin diseases are treated with ointments or creams. In inflammatory diseases such as vascular inflammation, immune diseases, asthma or cancer, therapy is carried out by administering the drug.
Herbal, Natural & Pharmaceutical Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are divided into three groups. Decisive for the classification are their biological effect and the place of education. A distinction is made between mineral corticoids (e.g. aldosterone), which are also formed in the adrenal cortex and regulate the potassium-sodium balance and thus the water content of the body, glucocorticoids (e.g. cortisone) and steroid hormones (androgen and estrogen).
Glucocorticoids fulfill important tasks in the glucose, lipid and protein metabolism. Deficiency can lead to glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. For this reason, an increased intake of vitamin D, vitamin C and K, as well as magnesium and zinc should be ensured when taking it. The need for vitamins D and C in particular is greatly increased by the administration of glucocorticoids. Omega-3 fatty acids, on the other hand, can reduce the need for glucocorticoids. This should always be done in connection with a specially balanced diet.
The starting material for all corticosteroids is cholesterol. The synthetic corticosteroids include prednisone and prednisonol. Corticosteroids are converted in the liver and then excreted in the urine and bile.
Risks & side effects
Side effects can occur, especially if the dose is long or too high. Become artificial to the body Corticosteroids supplied, this leads to a decrease or the cessation of the body's own production. The intervention in the glucose metabolism can lead to changes in the fat metabolism (trunk obesity, moon face).
It is not uncommon for gastrointestinal ulcers and wound healing disorders to occur. Central nervous functions are at great risk. Under certain circumstances, this can lead to an increase in pressure or clouding of the lens of the eye. Used with care and with regular monitoring, nothing stands in the way of taking cortisone and other corticosteroids for a long time.


.jpg)

























.jpg)